.png)
In any industry, supply chain optimization is essential. Supply shortages are one of the most challenging aspects of metal manufacturing. Long wait times, high demand, and increased associated costs all contribute to delays. Supply chain management and optimization in metal fabrication is the ultimate form of collaboration, and organizations are constantly striving to improve in this area in order to pass savings on to customers.
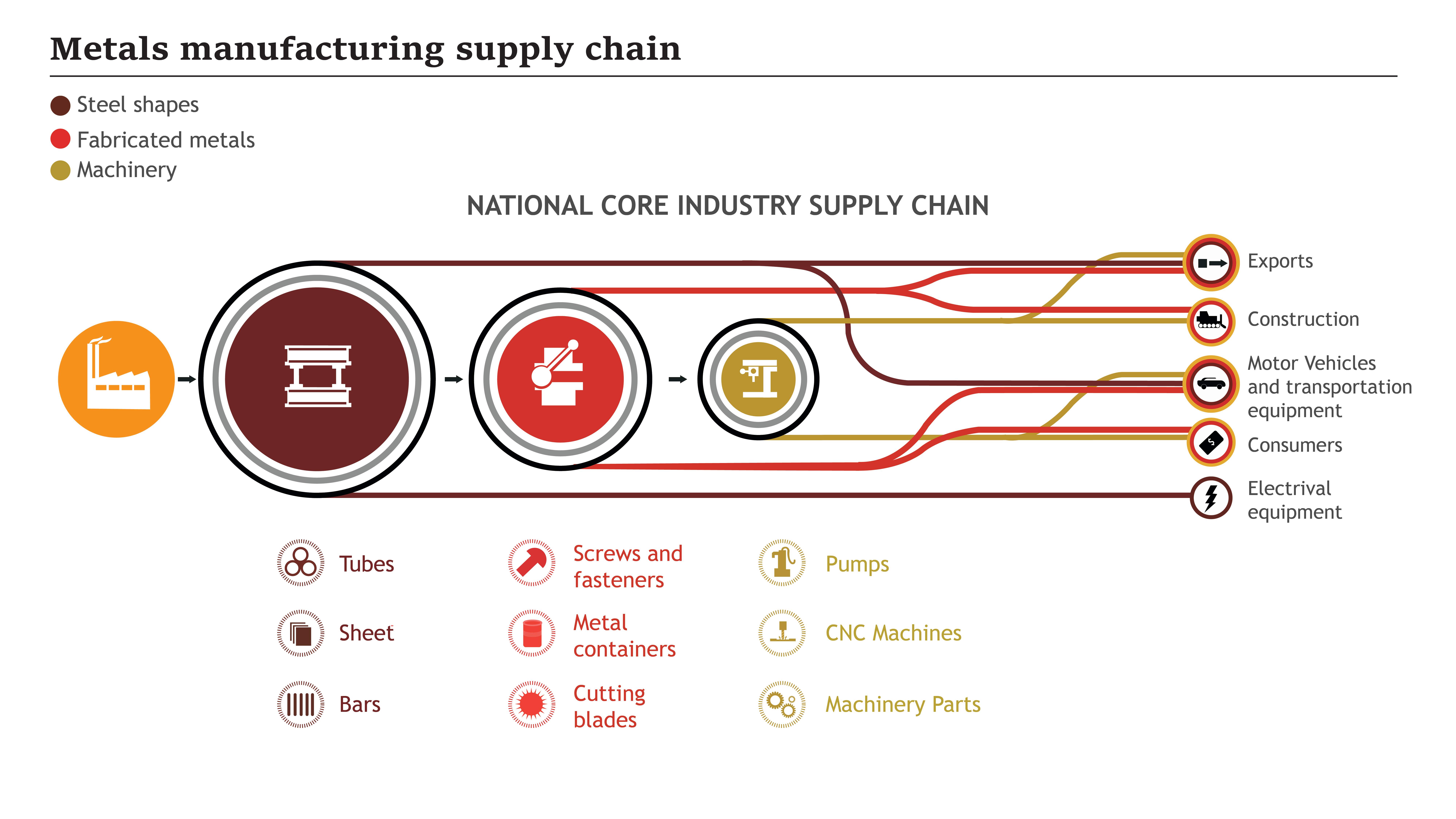
The fabricated metals industry faces challenges due to global supply chain disruptions, workforce shortages, cost increases, regional instability, and uncertainty. The industry's raw materials, inbound logistics, manufacturing floor, and outgoing warehouse have all been impacted by the shift from surplus to global scarcity. Research shows that 82% of metal manufacturing companies have encountered material handling and supply chain issues, reducing profit margins. Only 12% of organizations have systems supporting external communication, and 18% have systems for order configuration and product design. These issues require alignment of worker capabilities, manufacturing schedules, and material availability to meet customer expectations.
The blog examines the issues that metal fabricators confront in the fabricated metal sector, such as uncertain markets, offshore price cuts, and rising customer demands for quality, speed, and customization, and provides solutions to help producers adapt and survive. Additionally we will explore the various strategies and techniques that organizations can implement to optimize their supply chain in metal fabrication. From streamlining procurement processes to enhancing communication with suppliers, we will delve into the key steps that can help reduce supply shortages and improve overall efficiency in the industry.
Supply chain optimization is the process of improving the structure and operation of a supply chain. It strives to maximize the utilization of resources and technology in order to improve the efficiency and performance of the supply chain. Well-optimized supply chains enable firms to achieve their broader goals, such as increasing profit or building resilience to external situations.
• There are three main phases: design, planning, and execution.
• Design entails building a supply chain network, analyzing needs, establishing goals, and planning fulfillment operations.
• Planning entails developing a supply chain strategy to improve network efficacy, such as inventory management and asset deployment.
• Execution entails continuous management of supply chain activities, supplier management, supply chain financing, visibility improvement, and performance evaluations.
Sheet metal fabrication is essential for producing electronic devices and in industries such as construction, aircraft, and automotive. It provides critical parts. As the market for this industry expands, time and cost optimization in sheet metal manufacturing becomes critical. Efficient manufacturing procedures result in shorter production cycles, lower costs, and higher product quality. Manufacturers can achieve maximum efficiency by simplifying the production process, which includes design considerations, material selection, tooling, automation, and workflow optimization. These tactics can improve bespoke metal manufacturing, eliminate waste, shorten lead times, and provide a competitive advantage in the fast-paced electronics business.
1) Costs of Raw Materials:
2) Transportation and Logistics Expenses: Shipping, freight, and customs duties; these costs can be greatly impacted by the mode of transportation and the routes chosen.
3)Labor Costs: Manufacturing in areas with high labor costs raises the overall cost, whereas locations with reduced labor costs can lower it. Labor costs have a substantial impact on the final cost of a good or service.
4)Costs Associated with Regulatory Compliance:
5)Investments in Technology and Innovation: Adding cutting-edge technologies to the supply chain can raise expenses at first but lead to long-term efficiency improvements.
6)Market Demand and Supply Dynamics:
7)Currency fluctuations: The costs incurred by businesses engaged in international trade can be significantly impacted by changes in exchange rates.
8) Building solid connections with suppliers and employing successful bargaining techniques can have a significant impact on the cost of procurement.
Increasing production line efficiency is essential to meeting the metal industry's growing demands. An industry analysis estimates that between 2023 and 2027, metal component and application production efficiency would rise by 5%. This helps manufacturers meet the growing demand. Industry 4.0 technology, which can increase production, cut waste, and speed up decision-making, can help achieve this. By reducing the amount of time spent on manual tasks, automation—such as robotic bending machines—can also boost productivity.
Another crucial component of cutting waste in the sheet metal manufacturing process is cost reduction. Bulk creation, energy efficiency, preventative maintenance, and quality control can all be combined to achieve this.Frequent upkeep and service of machinery can extend its lifespan and increase uptime by preventing expensive repairs and failures.
Accreditations and rules from the government can help improve the quality of metal production. Purchasing a specific ISO accreditation can guarantee that the final component is subjected to stringent quality control and inspection processes for component buyers. For food processing equipment, a company aiming to meet the AS9100 group of standards may need to obtain alternative health and safety accreditations or quality equivalent to BS EN 1672-2:2005.
Supply chains for the manufacture of sheet metal must be optimized in order to satisfy the industry's rising demand. This entails combining technological know-how with industry-leading technology to guarantee a seamless, effective, and high-quality supply chain.
Lastly, sheet metal fabricators can profit from implementing Industry 4.0 by digitizing their supply chain processes. Online metal marketplaces, such as Metalbook, provide several advantages, including increased efficiency and enjoyment.
Furthermore, fabricated metal purchasers can save time and money on sheet metal fabrication by digitizing the entire procurement process, as well as focusing on design, material selection, tooling, automation, and workflow optimization. By implementing these tactics, they can improve their manufacturing processes, remain competitive, and efficiently produce high-quality electronic products.